

- Changchun Rongde Optics
- Co.,Ltd.
- Add:No.1666 Yaan Road,
- North Lake Development District,
- Changchun 130102,China
- Tel:86-431-81881745
- Fax:86-0431-85256892
- E-mail:rongdecui@roundss.net
- Skype:adacui_roundss
Company News
Current position :Home > News > Photoelectric Sense
What is the advantage of absolute encoder!
Changchun Rongde Optics Co.,Ltd. Release time:2017/11/24 Browse:1064
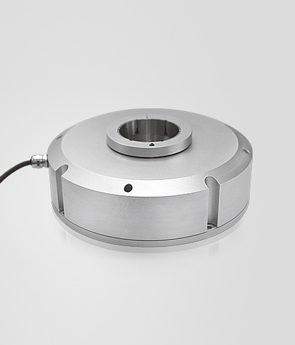
Absolute encoder The biggest disadvantage of incremental encoders is that they do not track any incremental changes output by the encoder when the system is powered down (for example, a temporary blackout). Therefore, in order to provide accurate position data, incremental encoders must be returned to their original position upon start-up. For applications where the conveyor is shut down every night and then restarted each morning, the incremental encoder returns to its original location without impacting the application. However, in automotive applications such as robotic arm applications, returning the incremental encoder to its home position can severely damage the product and the robot arm when the seat brackets are powered down. Absolute encoders are ideal for high-reliability applications. Unlike incremental encoders, absolute encoders do not output pulses. Instead, they output digital signals to indicate the encoder position and the encoder position as a static reference point in the absolute coordinate system. Therefore, the absolute encoder can still save its absolute position record while power is off. Restart the system immediately after exercise, without returning to the initial position. The absolute value rotary encoder has a code wheel attached to the shaft and a fixed grating that allows the system to generate a unique binary identifier for each stroke point (the linear sensor works similarly, for the sake of simplicity, Focus on rotary encoders). As the code wheel is rotated onto a fixed raster, the system periodically reads the identifier and outputs it as a multi-bit digital signal. The associated controller or frequency converter can poll the encoder to capture the position data and can use it directly or process it as speed information. Optical encoders have alternating transparent and opaque areas on the fixed raster, and likewise, there are transparent and opaque areas on the code wheel, forming a set of code coils (code tracks) and forming radiation zones on the code tracks (see Figure 3); Each code track is read by a pair of different LED light / light sensors. The code wheel, located on the top of the fixed raster, is usually located on the top of a sensor-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that contains the detector matrix and associated electronics. As the code wheel rotates, the transparent area of the code wheel periodically coincides with the clear area of the fixed grating, allowing the light signal to reach the detector and generate a pulse. Each track on the code wheel corresponds to a bit in the output; when the number of tracks is n, 2n radiation positions can be generated. The absolute standard resolution of an absolute encoder is 12 bits, or 4096 positions per revolution. In addition, some models offer 22bit (4.19 x 106 positions) or higher resolution. Magnetic encoders work similar to optical encoders. Some applications involve long-distance movement, which requires the use of a multi-turn coder. At this point, the second coder (or more) engages the main coder to track the number of rotations of the main coder. After each main encoder rotation, the 2nd encoder is indexed. This design assigns a unique coordinate - up to 4096 turns - for each position of the center axis of the index encoder. Applications using absolute encoders are often complex and require the deployment of hardware and software to interact with other electronic devices (PLCs, frequency converters, etc.) in the system.
newmaker.com
Figure 3: Optical Absolute Encoder resolution for each bit corresponds to a code wheel in the code track. The number of digits n (2n) is equal to the 2n radiation position. Corresponds to channel B; note that their phase difference is 90 °.
newmaker.com
 Previous:How to connect encoder to servo drives?
Previous:How to connect encoder to servo drives? Next:How to connect encoder?
Next:How to connect encoder?

















 Products
Products